
In this tutorial, we will learn what is the difference between different system shutdown commands used in Oracle Solaris operating system which are being used by System Administrators.
System Administrators perform many tasks in their routine work. Shutting down or rebooting the system is one of those tasks, and It is one of the risky tasks for them because sometimes the system won’t come back due to some reasons and they need to spend more time on it to troubleshoot.
Today we will learn about these shutdown commands available in Oracle Solaris operating system so that Administrators can choose the appropriate command to perform the task based on their requirements.
Shutdown Commands
To shut an oracle system down, one of two commands are typically used: shutdown or init. Both commands perform a clean shutdown of the system. Both start processes that write all file system changes to disk and terminate all system services, processes, and the OS.
- shutdown is typically used on systems running in the multiuser state. If used without options, the command brings the systems to run level S (single-user) by default.
- init is best used on stand-alone systems where other users are not affected by any shutdown. It does not send out notifications about the pending shutdown and completes the shutdown process faster.
Learn more about Solaris Run Levels here.
For example, to reboot the system using shutdown command, use below command:
# shutdown -i S -g 120 "===== disk replacement ====="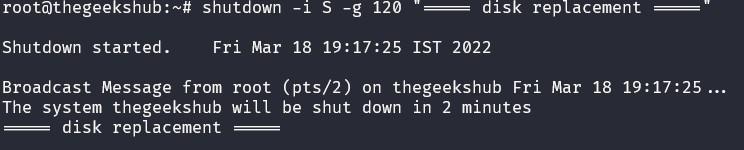
In the example, the shutdown command is being scheduled in 120 seconds. The warning message is output 2 minutes, 1 minute, and 30 seconds before the final confirmation message.
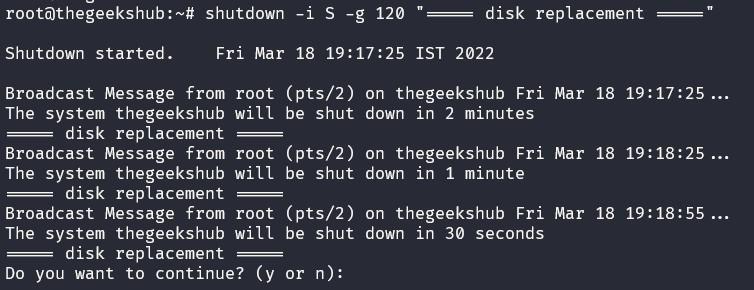
Various shutdown commands
The following table describes the various shutdown commands used in Solaris OS and provides recommendations for using them.
Reference Links:-
- https://docs.oracle.com/cd/E37838_01/html/E60978/runlevels-130.html
- https://docs.oracle.com/cd/E23824_01/html/821-1451/hbrunlevels-13026.html





